Ice exposed: Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter image of Mars

Overview
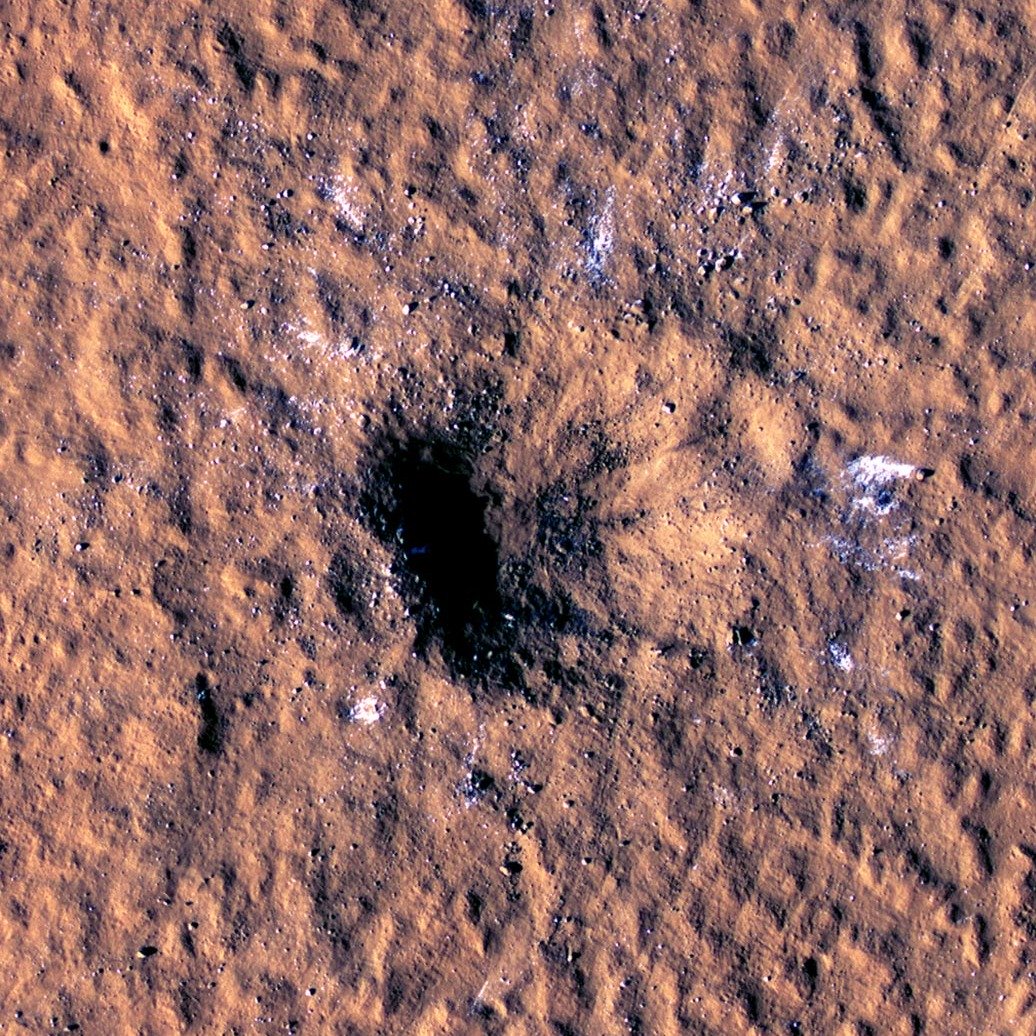

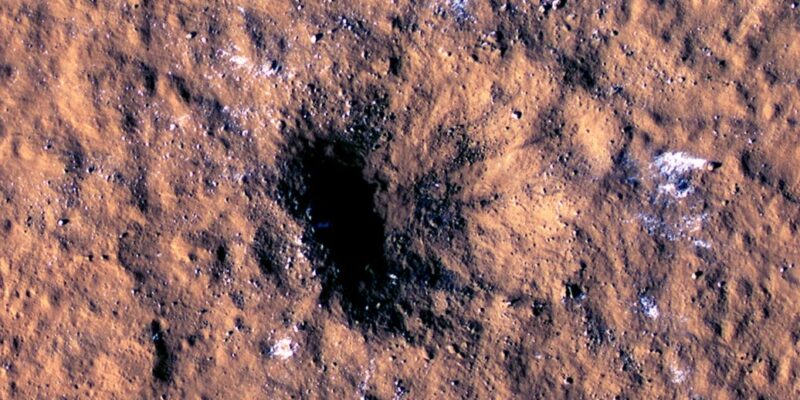
A new image of the impact crater taken by the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter ( MRO )
NASA has released a new image of the impact crater taken by the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter ( MRO ), showing the white patches of subsurface ice that have been exposed by meteorites. The impact crater, which hit on December 24, 2021, is 150 meters in diameter and 21 meters deep.
The impact triggered a Martian earthquake of more than magnitude 4, making it the strongest meteorite impact ever recorded by NASA’s InSight.
Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter

Artist’s impression of the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter spacecraft.
Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter[1] ( MRO ) is a spacecraft designed to study the geology and climate of Mars, provide reconnaissance of future landing sites, and relay data from surface missions back to Earth.
MRO has both scientific and ” mission support ” objectives.
- The formal science objectives of MRO are to:
- observe the present climate, particularly its atmospheric circulation and seasonal variations;
- search for signs of water, both past and present, and understand how it altered the planet’s surface;
map and characterize the geological forces that shaped the surface.
The two mission support objectives for MRO are to:
- provide data relay services from ground missions back to Earth;
- characterize the safety and feasibility of potential future landing sites and Mars rover traverses.
MRO played a key role in choosing safe landing sites for the Phoenix lander ( 2007 ), Mars Science Laboratory / Curiosity rover ( 2012 ), InSight lander ( 2018 ), and the Mars 2020 / Perseverance rover ( 2021 ).
InSight
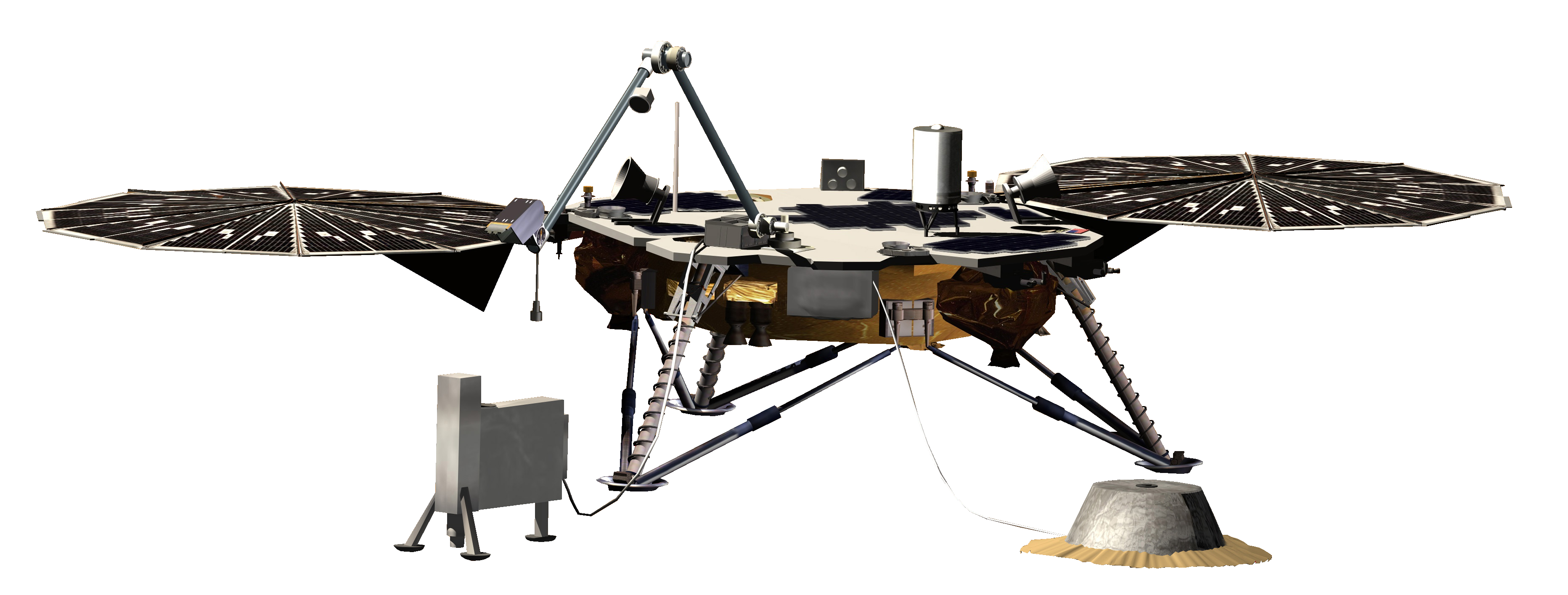
InSight
The Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations[2], Geodesy and Heat Transport ( InSight ) mission is a robotic lander designed to study the deep interior of the planet Mars.
InSight’s objectives are to place a seismometer, called Seismic Experiment for Interior Structure ( SEIS ), on the surface of Mars to measure seismic activity and provide accurate 3D models of the planet’s interior; and measure internal heat transfer using a heat probe called HP3 to study Mars’ early geological evolution.
This could bring a new understanding of how the Solar System’s terrestrial planets – Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars – and Earth’s Moon form and evolve.
References :