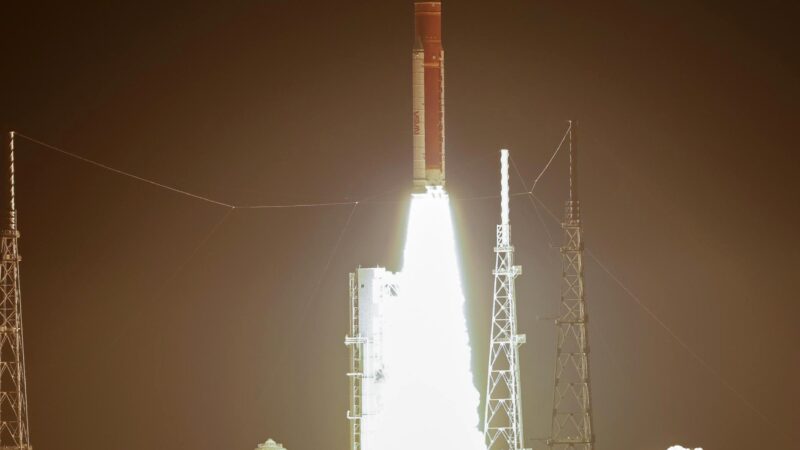
AngoSat 2 : Russia will launch a satellites for Angola

Overview
The AngoSat 2 will launch atop the Proton M rocket, lifting off from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan, replacing the failed AngoSat 1.
Angola
Angola[1] ( /ænˈɡoʊlə/ ( listen ); Portuguese : [ɐ̃ˈɡɔlɐ]), officially the Republic of Angola ( Portuguese: República de Angola ), is a country located on the west coast of Southern Africa.
It is the second-largest Lusophone ( Portuguese-speaking ) country in both total area and population ( behind Brazil in both cases ), and is the seventh-largest country in Africa.
AngoSat 1
AngoSat 1[2] was a geostationary communications satellite operated by Angosat and built by the Russian company RKK Energia.

RKK Energia.
It was the first communications satellite of Angola, designed for a 15-year mission to deliver television, internet, and radio services to Angola and other territories. The satellite suffered a power problem in the first hours of flight and lost contact with ground control. After the power problem, contact was established with the satellite, but ultimately the satellite did not recover, and contact was lost permanently 3 days into the mission. After repeated failures to establish contact in the following weeks/months, the satellite was declared lost. Russia will build a replacement satellite called AngoSat 2 to be delivered in late 2019.
AngoSat 2
The AngoSat 2 is an Angolan communications satellite built to replace the failed AngoSat 1. The satellite is part of the AngoSat Project which is working on developing communications satellites equipped with C- and Ku-band transponders which will operate in geostationary orbit, as well as developing ground communications and broadcasting infrastructure.
It was expected that the AngoSat 2 would be identical to the original AngoSat 1, however in August 2019 it was revealed that the replacement would be built by ISS Reshetnev ( Bus ) and Airbus Defense & Space ( payload ). The satellite has an expected lifespan of 15 years.
Proton-M

Proton-M
The Proton-M[3], ( Протон-М ) GRAU index 8K82M or 8K82KM, is an expendable Russian heavy-lift launch vehicle derived from the Soviet-developed Proton. It is built by Khrunichev, and launched from sites 81 and 200 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Commercial launches are marketed by International Launch Services ( ILS ), and generally use Site 200/39. The first Proton-M launch occurred on 7 April 2001.
Proton flew its most recent mission on 13 December 2021, launching two Ekspress communication satellites into geostationary orbit. As of August 2020, a number of Roscosmos and other Russian government missions remain on Proton launch manifest.
References: